
ECE 499 - GROUP 3
Electronically Controlling a Smart Bike Tensioning System Using Bluetooth
WHO WE ARE
Steven Dashuck V00874539
Jordan Carlson V00714886
Duncan Cairns V00888276
Hien Van To V00948322
(from left to right)


WHAT WE DO
-
Create an inexpensive and long-term solution (lasting 5+ years within the under-desk bike) that will replace an existing, hand knob tensioner system within the Ergonomyx Technologies under-desk bike system with an electronically controlled Bluetooth pedal-tension system.
-
Utilize the existing under-desk bike’s proprietary, pedal powered generator and connect to a mobile device through Bluetooth to transmit pedaling tension adjustments and receive the status of the pedaling tension.



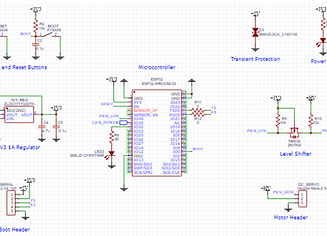

Electrical Design
-
The circuitry was designed to distribute the power from the 3-phase AC generator to power the DC Servo motor.
-
The microcontroller is powered by an external power supply so that the microcontroller does not lose power when the user stops pedaling
Mechanical Design
-
3D printed PLA case for the servo motor to be mounted on the bike frame that can withstand full torque 9.4kgf.cm from the servo motor
-
The rotary head mounted on the motor is designed to provide an adequate traveling distance for the magnet arrays with a 120 rotational degrees limit
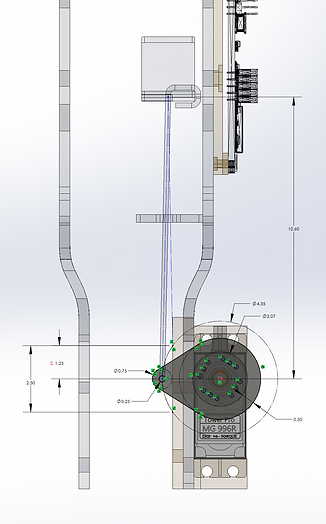

.jpg)
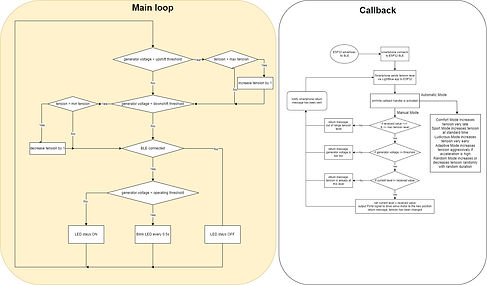
Firmware
-
Programmed in C++ over a C microcontroller framework
-
Enables and configures the proper BLE Generic Attribute Profile (GATT) of the ESP32 microcontroller
-
Generates a 5V PWM signal to drive the servo motor
-
Monitor generator voltage to adjust the suitable tensioning level on both manual and automatic modes
Learn more [7]
Integration Testing and Troubleshooting
-
Needs a minimum of 7.5V from the generator to operate the servo motor properly
-
Reduces tension when voltage drops below 8.25V
-
Has 10 different tension levels for Manual Mode
-
Has 5 Automatic Modes: Comfort, Sport, Ludicrous, Adaptive, and Random
-
Notifies the user's smartphone to confirm any mode change

Future works
1 / Implement the motor driver board on Ergonomyx's board
Using the same microcontroller on the bike to control the tension level requires both electrical and firmware integration, which would require changed so the current Ergonomyx under-desk bike PCB.
2 / Create a dedicated menu on the Ergonomyx app for tension adjustment
The menu would increase ease-of-use. It should have a slider to display and select the tensioning level in manual mode and a toggle switch to select each automatic mode.
3 / Design a larger case for the servo motor
To fit the servo motor more securely for increased durability.
4 / Combine the original tension adjustment knob with an electronic adjustment system
Would allow users to still use manual adjustment when the smartphone is not available.
Acknowledgement
Faculty supervisor: Dr. Ilamparithi Thirumarai Chelvan
Co-supervisor: Sergio Pérez Martell
We specially thank Ergonomyx Technologies Inc. for allowing us to use their soldering space and meeting venue.
References
[1] “PCB Design,” EasyEDA(standard) - a simple and powerful electronic circuit design tool.
[2] “Circuit Schematic,” EasyEDA(standard) - a simple and powerful electronic circuit design tool.
[3] Ergonomyx, “Smart Under Desk Bike,” ERGONOMYX, 2022. [Online]. Available: https://www.ergonomyx.com/products/smart-under- desk-bike. [Accessed 23 June 2022].
[4] Datasheet, TS2596, “3A / 150kHz Step-Down DC-DC Converter”, Taiwan Semiconductor.
[5] Dassault Systemes, "Inserting and Resizing Sketch Pictures," 2022. [Online].
[6] Tower Pro, “MG996R,” 2014. [Online]. Available: https://www.electronicoscaldas.com/datasheet/MG996R_Tower-Pro.pdf. [Accessed 24 June 2022].
[7] “Esp32 Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) on Arduino Ide,” Random Nerd Tutorials, 04-Jun-2019. [Online]. Available: https://randomnerdtutorials.com/esp32-bluetooth-low-energy-ble-arduino-ide/. [Accessed: 27-Jul-2022].